In caves atmosphere such gases can be met not sparsely, which, it seems, may have no connection with underground world. Among those gases there are methane, hydrogen [17], as well as more than usually carbon dioxide concentrations [17],[25],[52],[92].
It isn't the first time, when high concentration of methane and carbon dioxide brought to human victims in caves [20]. So, the problem comes out of only scientific circuits and becomes the problem of guarantee of human security under the ground in general.
Investigations of the caves, containing methane lefts several general peculiarities of caves, mentioned above, those are: existence of the organic substance and 100 % of humidity.
In nature methane occurs in several ways, one of which is so called biogas ( methane : carbon dioxide mixture ). It occurs in without oxygen ( anaerobic ) conditions, subjecting the organic raw material with methane bacteria fermentation [93].
The following types of digestion are distinguished according to the temperature:
- psychrophilic digestion ( 10 - 20OC, retention time is over 200 days ),
- mesophilic digestion ( 20 - 36OC, retention time is over 20 days ),
- thermophilic digestion ( 50 - 60OC, retention time is about 8 days ).
In order to calculate CH4 and CO2 quantity occurring on the basis of chemical form of the decomposing substance beforehand, the following equation is proceeded [94]:
CnHaOb + (n-a/4-b/2 ) H2O = (n/2-a/8+b/4)CO2 + (n/2+a/8-b/4)CH4.
The methane content depends on the feeding material, some typical values are as follows:
cattle manure -65%,
poultry manure -60%,
grass -70%,
leaves - 58%,
algae - 63%,
water hyacints - 52%.
The remains of grass and trees and bushes subjected to anaerobic fermentation are richer with phosphorus than poultry manure ( guano ).
When guano and solid substances are mixed with each other, correlation of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, which is left after fermentation in the massif, form N : P2O5 : K2O = 1 : 0,5 : 1. During the digestion process, gaseous nitrogen is converted to ammonia ( NH3 ). Phosphorus generates phosphoric minerals and potassium generates potassium minerals [95].
Biogas is somewhat latter, than air density-0,94 kg/m3 and has an ignition temperature of approximately 700OC. The temperature of the flame is 870OC. Biogas consists of about 60% methane and 40% carbon dioxide. It also contains small proportions of other substances, including up to 1% of hydrogen sulphide.
Feed materials consist of organic solids, inorganic solids, water. The biogas is formed by digestion of the organic substances. The inorganic materials ( minerals and metals ) are unused ballast, which is unaffacted by the digestion process.
The water makes feed materials capable of flowing. This is important for the operation of a biogas plant. It is easier for the methane bacteria to come into contact with feed material, which is still fresh, when the slurry is liquid. This accelerates the digestion process.
The cattle manure is made up of 16% of solids and 84% of water.
Decomposition of organic substances up to CO2 and CH4 takes place under the influence of three big groups of bacteria in parallel.
Fermentative bacteria are included in the first group. Fermentative bacteria subjected to hydrolysis the initial polymers ( polysaccharides, proteins, lipids ) of substrates, generating acetic acid and other saturated fatty acids, CO2 and H2 [96],[97]. It is necessary for the concentration of hydrogen to be low for this process. In this case propionic acid and other fatty acids and fragnant acids decomposition up to acetic acid and hydrogen will be favorable thermodynamically [98] ( Figure 80 ).
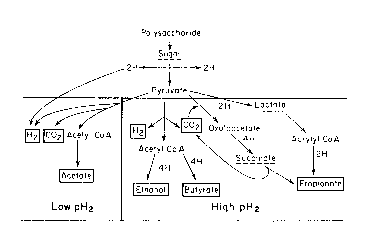
Figure 80. The main directions of final substances origin in the case of H2 low and high pressures ( PH2 ) and ways for carbohydrate decomposition by fermentative bacteria.
The second group of bacteria, so called generating H2 ( restoring proton ) acetogenic bacteria [98],[99] generate acetic acid, hydrogen and CO2.
The third group in general, methanogenic bacteria crack the acetic acid up to CO2 and CH4 and a part of them restore CO2 with hydrogen up to CH4 [100],[102].
The three phases scheme of anaerobic decomposition is given in Figure 81 [98].

Figure 81. The three phase scheme of organic substances anaerobic decomposition: 1 - fermentative bacteria, 2 - H2 generating bacteria, 3 - methanogenic bacteria.