Performic acid is discovered in cave, containing organic substance ( mainly manure of birds and flying mice ), in rot organic remains as well as in caves air.
By mentioned above 26 reactions it is shown the role of HCO3H in those anaerobic processes, the final result of which is the decomposition of the organic substance and methane origin.
Unfortunately, the phenomenon of decomposition is not confined to that: HCO3H also decomposes and generates carbon dioxide gas.
In order to clarify the way of performic acid decomposition we synthesized it by [104] method. With that goal we added carefully 28,4 gr. of 90% H2O2 ( 0,75 mol ) to 23 gr. 100% formic acid ( 0,5 mol ), in which 0,28 ml thick sulphurous acid had already been soluted beforehand. The retort was placed in water bath ( T = 22-23 OC ). Performic acid occurs by oxidization of formic acid:
HCO2H + H2O2 = HCO3H + H2O.
Thirty minutes later HCO3H quantity reaches the highest value and forms 35%. Performic acid is got with formic acid mixture 0,29 mol:0,21 mol correlation ( 1 : 0,72 ).
Then performic acid - formic acid mixture was frozen up to -70 OC and CO2 existing in the solution was taken away carefully. After that we filled the mixture in a glass retort, heat it for 10 minutes on the water bath in 93 OC, then the retort was quickly frozen and then we investigated the content. Performic acid was entirely transferred into CO2 and water:
HCO3H = H2O + CO2.
In order to clarify with what kind of probability HCO3H goes through water solution to gas capacity and how it is subjected to future conversions there, it was necessary to know its vapors pressure. But performic acid is unstable combination and it exists only in a solution, at the same time with great number of formic acid, what makes the estimation of the ability of its vapors transference to the gas volume difficult. We overcame that ban, subjecting formic acid - performic acid system to mass - spectrummetring analysis [105]. The samples, subjected to analysis were installed in made of glass mobile trap of the mass - spectrum - meter. Pressure in the trap was 15 tor and in the box of ionization it was 10-7 tor. The mass - spectrum was taken out with the help of electronic beam containing 60 EV ( Electron Volt ) energy. First the mass - spectrum analysis for formic acid took place. With the goal of estimation of the background we added 0,28 ml thick sulphurous acid to HCO2H.
Then HCO3H - HCO2H mixture mass - spectrum metering analysis was done. The mass - spectrum which was receiving is given in Figure 83.
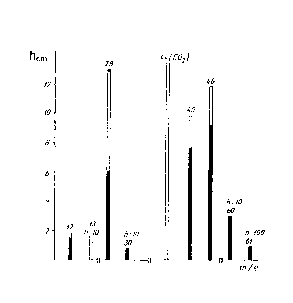
Figure 83. Performic acid - formic acid mixture mass - spectrum.
As it is seen from the Figure 83, the molecular peak of performic acid mass - spectrum, which had to have m/e = 62 ion value, is absent. There is a great peak m/e = 60 and a insignificant peak m/e = 61. Correlation of two peaks forms 20:1. Except those two peaks, the rest main peaks of HCO3H mass - spectrum coincide with HCO2H special peaks. Only m/e = 13 peak is the exception. It is related to formic acid. We used the height of this peak and managed to separate the mass - spectrums of performic acid and formic acid from each other. HCO3H mass - spectrum is given in the Table 16.
Table 16. The mass - spectrum of performic acid.
|
m/e |
the type of peak |
correlation of peaks ( % ) |
|
12 |
C |
16 |
|
29 |
HCO |
63,3 |
|
30 |
HCOH |
2 |
|
45 |
HCO2 |
83 |
|
46 |
HCO2H |
100 |
|
60 |
CO3 |
4,4 |
|
61 |
HCO3 |
0,22 |
With the help of the mass - spectrum meter we traced the decomposition of performoc acid in gas phase. Only during few minutes in the mass- spectrum given in the Figure 5 m/e = 60 the peak decreases. It means, that HCO3H decomposes quickly CO2 and water in the ionization box too, where the temperature is only 35 OC.
As it is seen from Figure 83, in the mass - spectrum of HCO2H the highest peak has m/e = 29 ion ( HCO+, 44 mm ). Correspondingly, HCO3H the highest peak has m/e = 46 ( HCO2H+, 58 mm ). HCO2H+ : HCO+ correlation forms 1:1,32. So in gas phase HCO3H: HCO2H correlation is 1 : 1,32. The correlation of the same substances makes 1,38 in liquid phase. The insignificant difference between 1,38 and 1,32 can be attributed to HCO3H quick decomposition in gas phase.
Consequently, the dates of mass - spectrum meter testify, that HCO3H has approximately the same pressure of saturated vaporous, as the formic acid has.
Dependence of performic acid saturated vapoures pressure, for known by formic acid revalue corresponding values [48], is given in Figure 84.
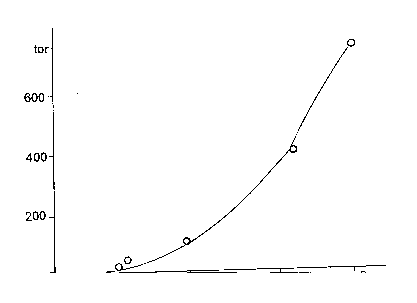
Figure 84. Dependence of HCO3H saturated vapours pressure on temperature.
Elucidation of performic acid decomposition mechanism becomes the question of special importance. It brought to an unknown phenomenon of nature discovered in Chemical Physics Institute of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Armenia,. The phenomenon is called: " The phenomenon of organic peroxides heterogeneous - radicals decomposition ".